Inverter
Creating a new entry
Create a data set by defining the various properties of the inverter on the subpages.
Basic data
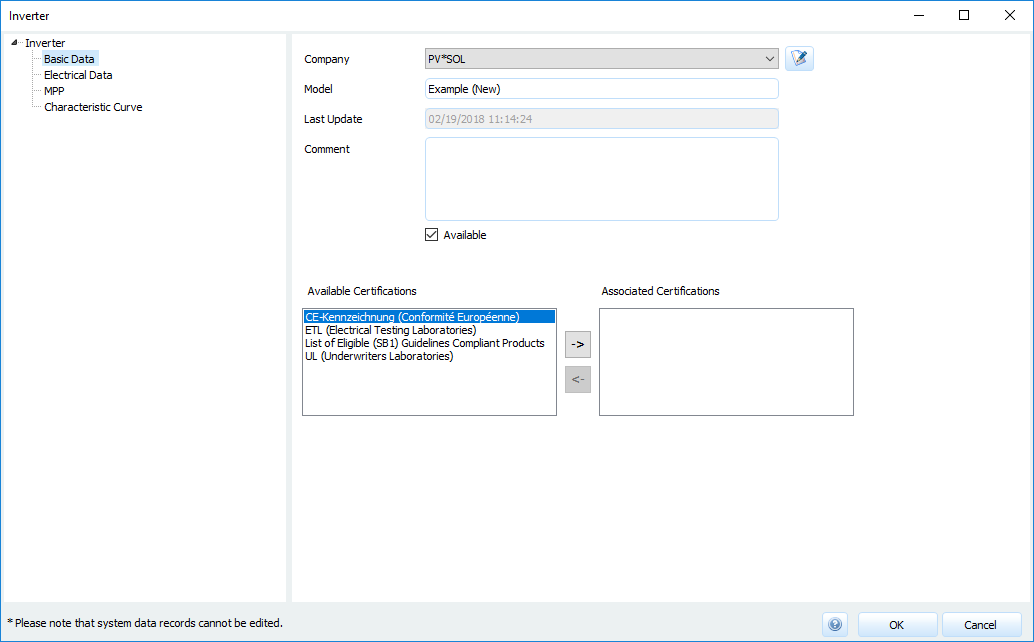
Inverter: Basic data
Choose company
With the button all companies can be displayed and new ones created.
all companies can be displayed and new ones created.Enter name for model
(optional) Insert comment
Determining whether the component is
 available.
available.
Components that are not available are hidden in the database view by default, but can be displayed again.(optional) Enter the available certificates
Electrical data
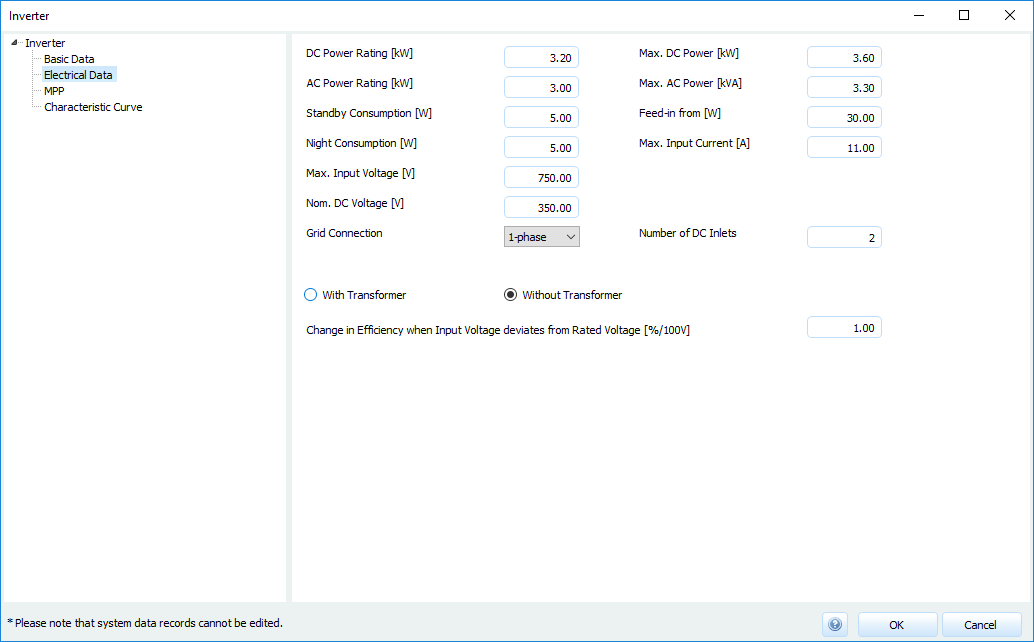
Inverter: Electrical data
Here you define the electrical data of the inverter.
Nominal DC power
The nominal DC power is the power for which the inverter is designed on the input side for continuous operation.Nominal AC power
The nominal AC power is the power for which the inverter is designed on the output side for continuous operation.Standby consumption
If the inverter does not supply energy to the grid or to the consumer, the inverter’s own consumption must be taken into account. In addition to standby consumption, there is also night consumption.Night consumption
The inverter switches off at night, but still requires a minimum of energy.Max. input voltage, Max. input current
This voltage limit or current limit must not be exceeded to protect the inverter. In PV*SOL® these limits are required for the configuration check, see Pages > Inverters > Configuration check.Nominal DC voltage
The rated voltage on the input side for normal operation of the inverter.Mains connection
- 1 phase
- split-phase
- 3 phase
Max. DC power , Max. AC power
Exceeding these power limits results in control of the PV output. In PV*SOL® these limits are also required for the configuration check, see Pages > Inverters > Configuration check.Feed in from
Minimum power that the inverter can feed into the grid.- Number of DC inputs
Galvanic isolation of the inverter
- With transformer
- Without transformer
Changing the efficiency in case of deviation of the input voltage from the nominal voltage The efficiency characteristic of the inverter is specified for the nominal voltage. If an inverter is not operated at nominal voltage, the efficiency of the inverter changes. The efficiency of an inverter decreases by the specified value per 100 V with deviation of the input voltage.
MPP
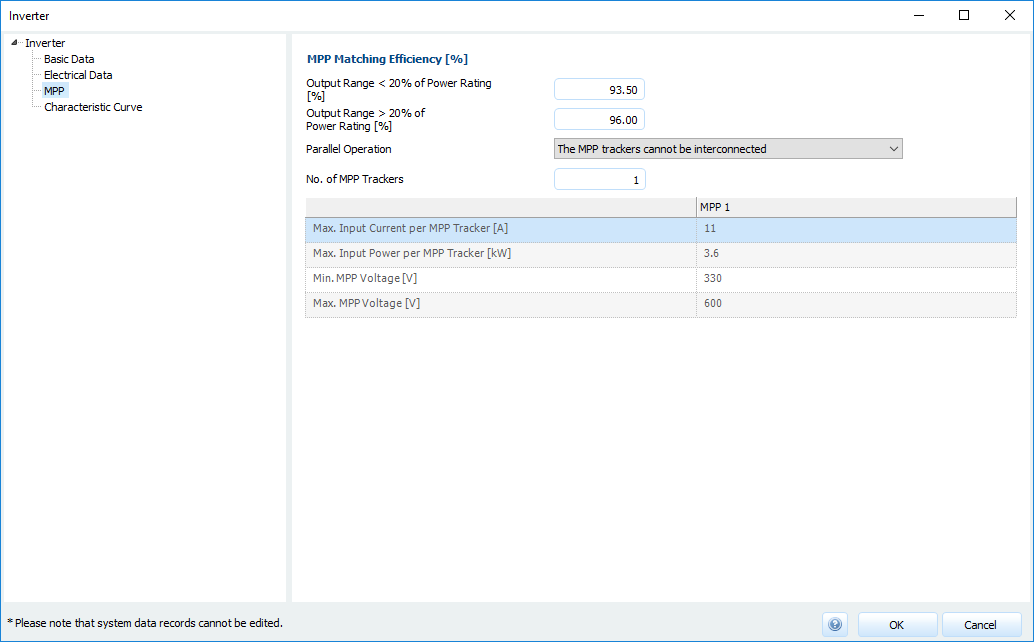
Inverter: MPP
Here you define the MPP-Tracker of the inverter.
MPP adaptation efficiencies
- Power ranges < 20% of rated power
- Power ranges > 20% of rated power
Parallel operation
- Interconnection of MPP trackers possible/not possible
- MPP trackers cannot be interconnected
- Either none or all MPP trackers are interconnected
- Number of MPP trackers
Data per MPP tracker:
- Max. Input current per MPP tracker
- Max. Input power per MPP tracker
- Min. MPP voltage , Max. MPP voltage
The MPP tracking of the inverter takes place within this voltage range.
Characteristic curve
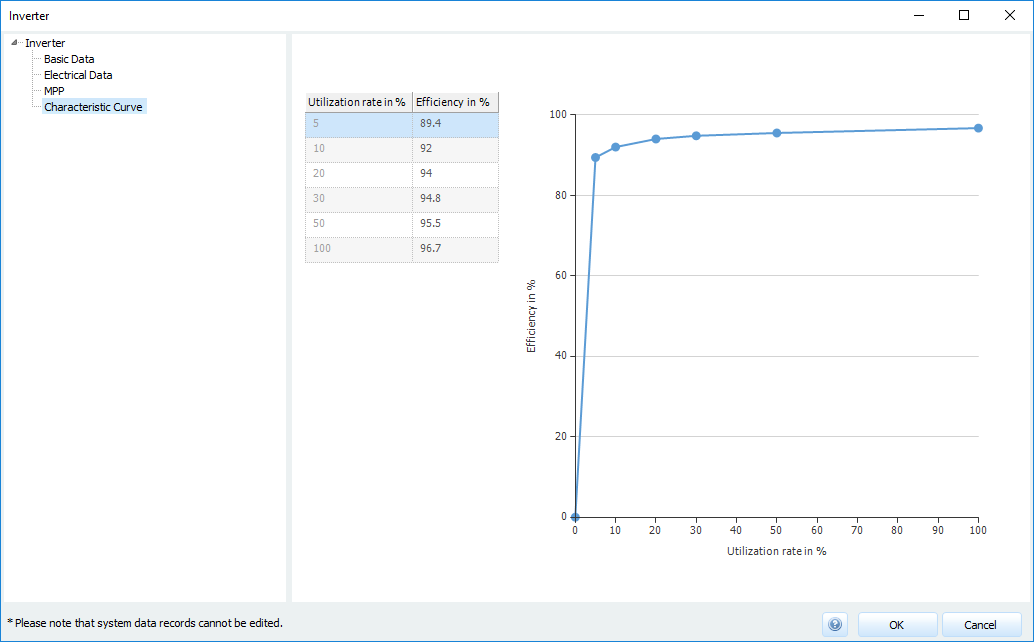
Inverter: Characteristic curve
To define the efficiency, specify the corresponding efficiency for all load ranges.
See also