Variant Menu: Preferences > Swimming Pool > Pool
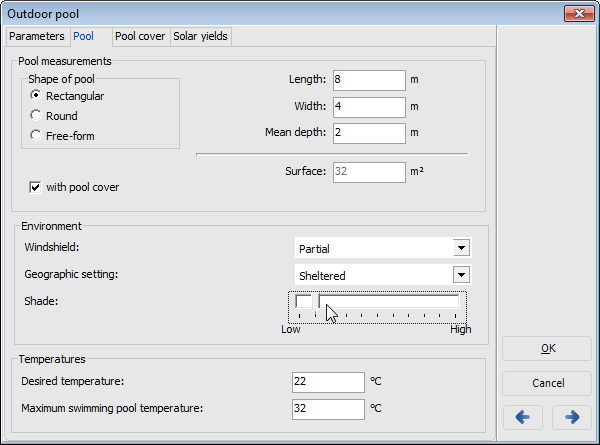
Image: Input dialog for the swimming pool, Pool page; Example: Outdoor pool
The primary determining factors for losses and gains are primarily the pool surface and, to a lesser extent, the pool shell insulation towards the ground. The volume is crucial for calculating temperature changes.
Dimensions
Enter the area or, for rectangular pool shapes, the length and width.
Specify the average depth. The volume will be calculated.
Indicate whether a cover is present.
Surroundings
Specify if there is a windbreak at the pool, reducing convection and evaporation losses.
Define the geographic environment of the swimming pool as:
- Very exposed (= in an open field),
- Exposed,
- Sheltered (= in a residential area), or
- Highly sheltered (= e.g., in a forest).
Specify the degree of shading.
Temperatures
Enter the desired temperature and the maximum swimming pool temperature.
The maximum swimming pool temperature is the temperature up to which the pool can be solar-heated. It must always be higher than the desired temperature. A higher maximum temperature allows for longer operating times of the collector loop, increasing the swimming pool heating demand and the coverage, as defined. The regulation of the auxiliary heating ensures that the pool is maintained with a hysteresis of 0.5 Kelvin.