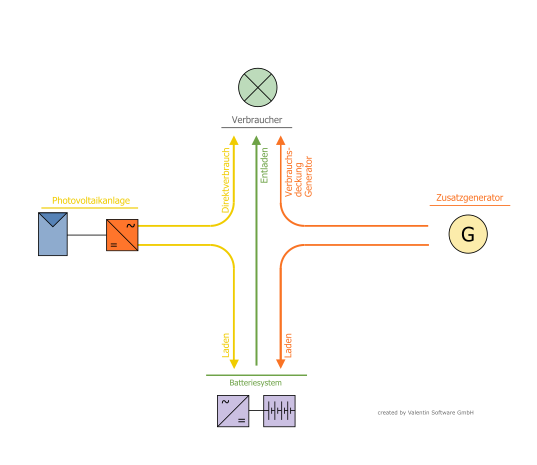
Offgrid systems
In off-grid systems, the main focus is on covering consumption. Since there is no grid that can cover the consumption when required, the PV system, battery system and - if available - the auxiliary generator must take over this task.
In contrast to grid-connected systems, load shedding can be set for the consumers of off-grid systems. Load shedding ensures that less important loads can be switched off when too little energy is currently available from PV, battery or auxiliary generator.
The energy of the PV system can also be controlled. This is necessary if the consumers and the batteries together cannot absorb as much energy as the PV system produces.
Energy Management
In off-grid systems, the following energy management determines when the energy is exchanged between the players in the system (PV, load, battery, additional generator if necessary).
-
Direct consumption
Consumption is directly covered by PV energy -
Discharging
Consumption is covered by the batteries- Up to the capacity limit of the battery system.
- Until the minimum SOC of the batteries is reached.
-
Consumption coverage of auxiliary generator
If the energy from PV and battery is not sufficient, the generator jumps in, if available -
Charging from the PV
Surplus PV energy is used to charge the battery.- Up to the capacity limit of the battery system.
- Until the maximum SOC of the batteries is reached.
-
Maintenance charge (charging from the generator)
Batteries are charged with energy from the auxiliary generator if charging methods are used to maintain the batteries (boost, full and equalisation charging) and PV energy is not available in sufficient quantities.
Load shedding
The consumers in PV*SOL® can be defined in different groups for off-grid systems. Usually, three groups are defined in more complex off-grid systems:
- without load shedding: Consumers belonging to the critical infrastructure, such as refrigerators, medical equipment, etc. These devices must always be able to be supplied with sufficient energy, otherwise the simulation will be aborted.
- Load shedding priority 1: Consumers that can be automatically disconnected from the island system, i.e. shedded, if there is a shortage of energy. e.g. non-critical computers, water pumps, etc.
- Load shedding priority 2: Consumers that are automatically disconnected from the stand-alone system when there is a shortage of energy, e.g. private TV sets or similar.
Load shedding is defined individually for each group and depends on the state of charge (SOC) of the batteries.Two time windows can be defined for each group.
The results show the difference between previously stated and actually covered consumption:
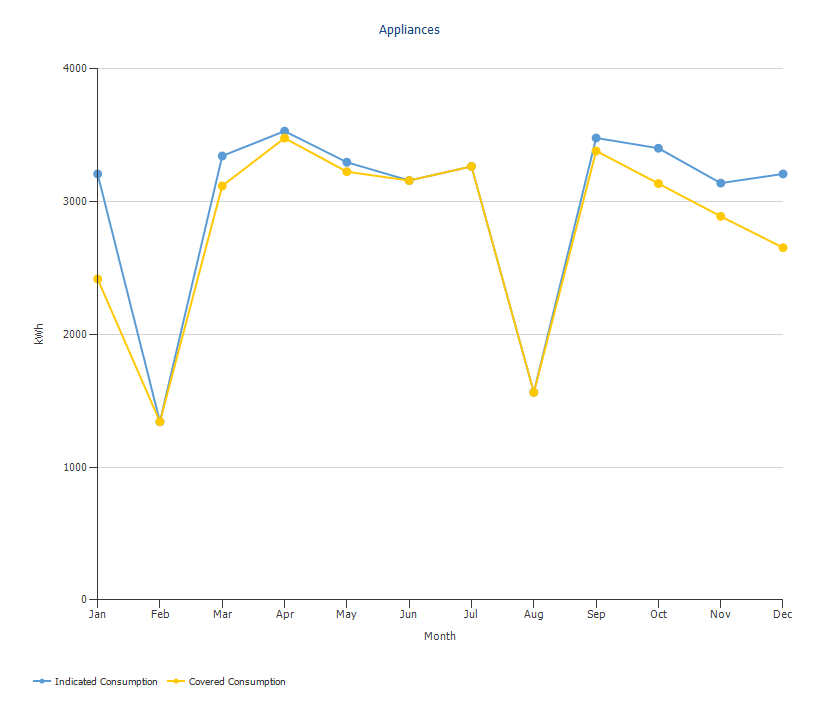
The difference between the defined load and the actual covered load after simulation of a grid-independent project.
Throttling of the PV system
If the PV system supplies more energy than can be absorbed by consumers and battery storage, the PV system must be throttled. This is done automatically. The results show the difference between maximum available energy and energy consumed:
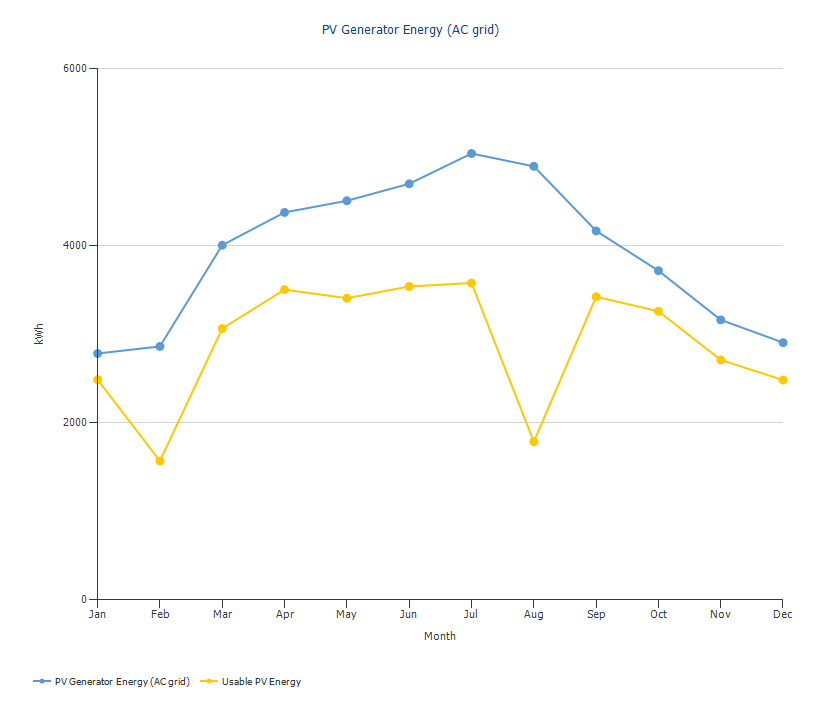
The difference between available PV energy and usable PV energy after the simulation of a grid-autonomous project.
See also