PV modules
Creating a new entry
Create a data set by defining the various properties of the PV module on the subpages.
- Basic data
- Electrical data
- I/V Characteristic values for STC
- I/V Part Load Characteristics
- Further parameters
- Mechanical variables
- Characteristics
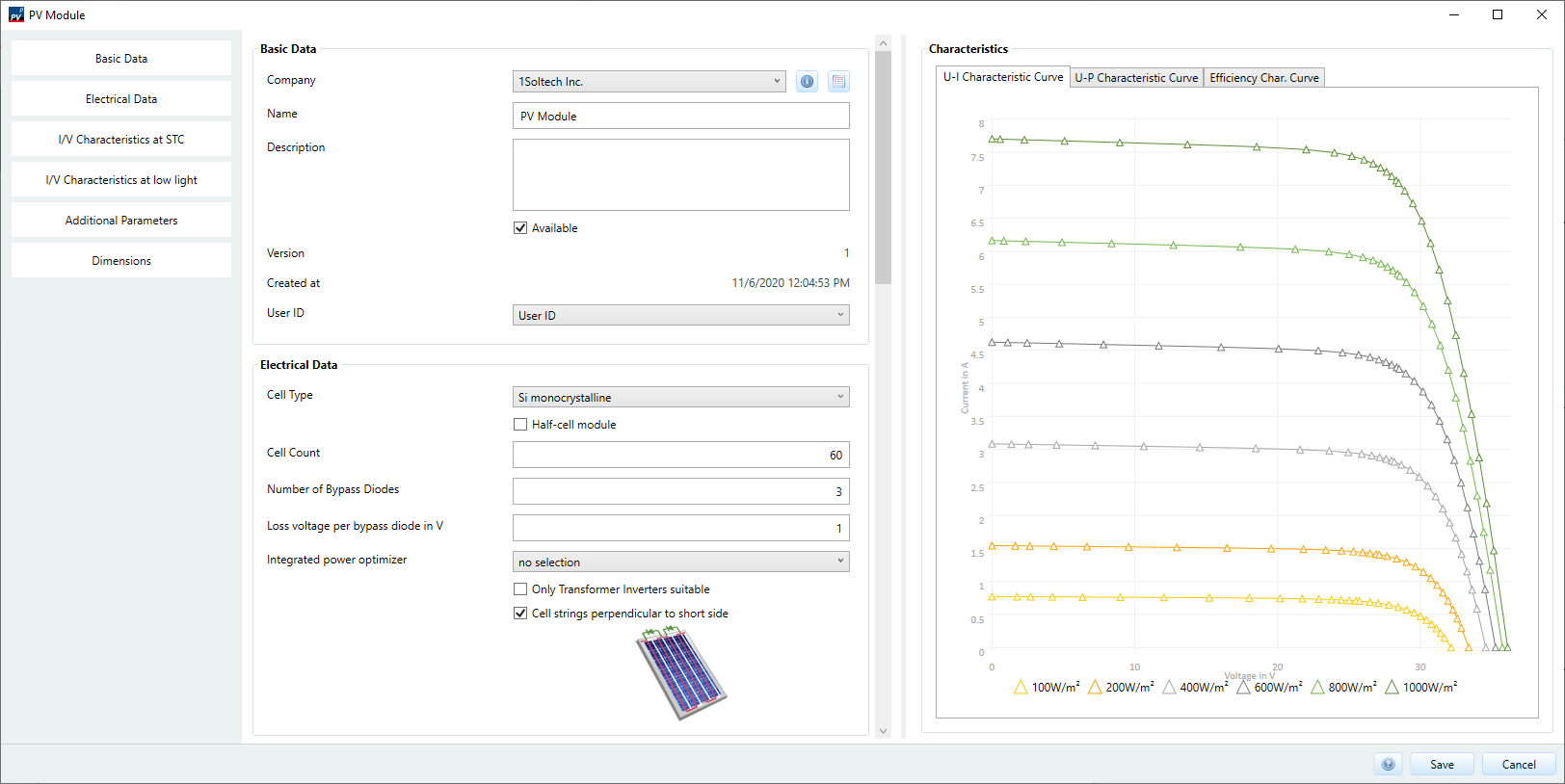
Basic data
-
Choose company
With the button all companies can be displayed and new ones created.
all companies can be displayed and new ones created. -
Enter name for model
-
(optional) Insert comment
-
Determining whether the component is
 available.
available.
Components that are not available are hidden in the database view by default, but can be displayed again. -
Enter the user ID to be used. The selected user ID determines the visibility of the record.
Electrical data
-
Specify cell type
- Si monocrystalline
- Si polycrystalline
- Si amorphous
- Other
- EFG
Edgedefined Film Growth, edge-defined layer growth, special manufacturing process for Si - Apex
PV modules from BP. No longer available. - Ribbon
PV modules manufactured using the String-Ribbon process. - HIT
Heterojunction with intrinsic thin layer, crystalline SI thin film, surrounded by ultra-thin amorphous SI - CIS
Copper indium gallium diselenide - CdTe
Cadmium telluride - triple a-Si
triple-junction Amorphous silicon thin film module - microcrystalline
Microcrystalline silicon
-
Specify number of cells
-
Specify number of bypass diodes
-
Specify Voltage loss per bypass diode
-
Integrated performance optimizer available?
You can choose from all available module-integrated power optimizers from the power optimizers database (see Databases > Components > Power optimizers). -
 Only suitable for transformer inverters
Only suitable for transformer inverters
Some PV modules may only be operated on inverters with galvanic isolation. -
Selection of the arrangement of the cell strands
- Cell strands perpendicular to the short side
- Cell strands parallel to the short side
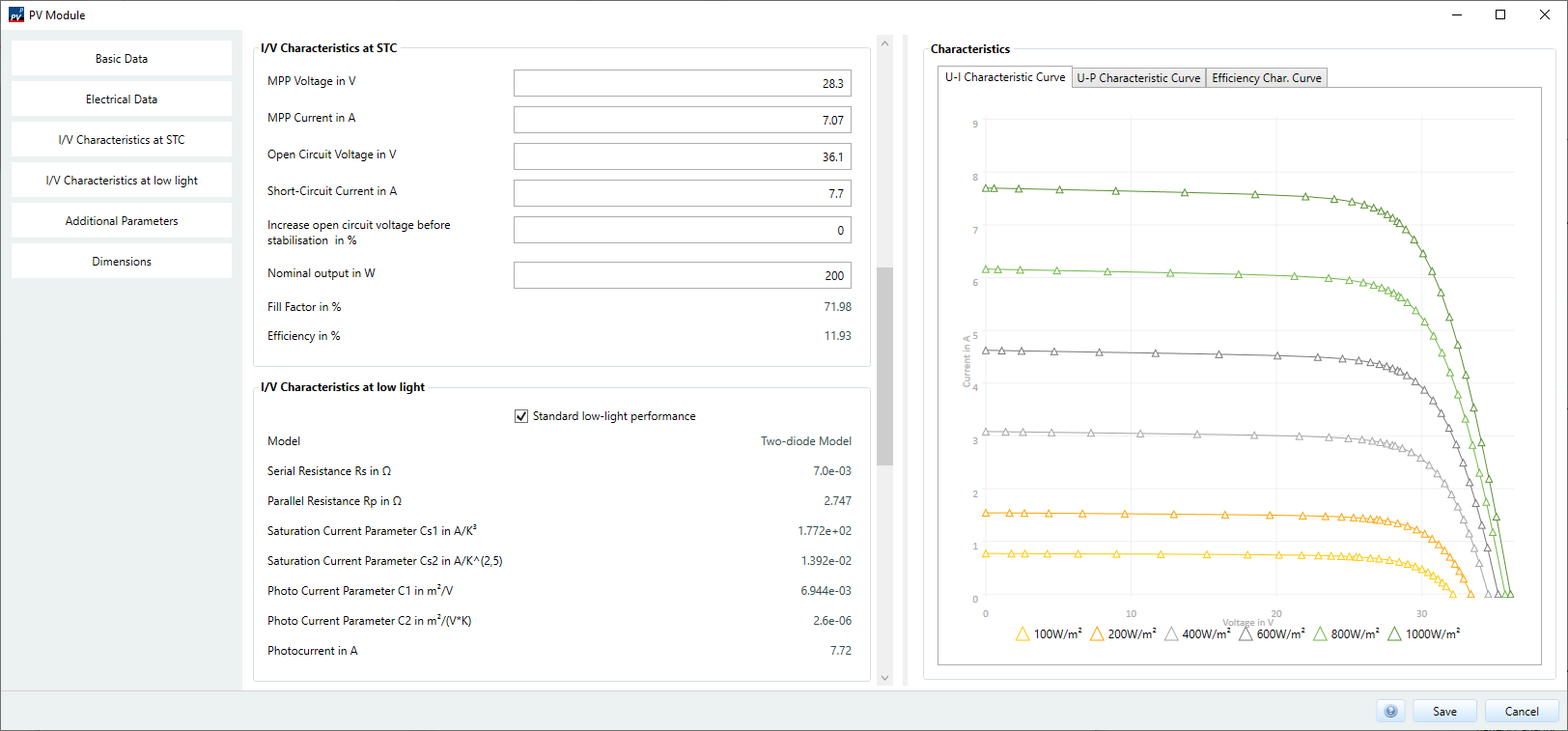
I/V Characteristic values at STC
The electrical characteristics of the PV module depend above all on temperature and irradiation. This results in a separate current/voltage characteristic curve for each module temperature and irradiation. In the range V/C Characteristic values at STC only characteristic values according to standard test conditions (STC) are entered.
All required characteristic values can be found on the data sheet of the corresponding PV module.
- Voltage at MPP
- Current at MPP
- Open circuit voltage
- Short circuit current
- Increased open circuit voltage before stabilization
This value specifies the proportion of the open-circuit voltage delivered above the specified STC open-circuit voltage. Then the configuration check is carried out (see Pages > Inverters > Configuration check). - Nominal power
I/V Part Load Characteristics
Here you define characteristic values of the PV module at lower irradiation. Since standard test conditions (STC) are not permanently available, the characteristic values at lower irradiation are important data for an exact simulation of the PV system.
To enter the partial load characteristic values, first select a partial load model:
- Manufacturer/own <br Here you can enter your own part-load characteristic values. The PV*SOL® model is used to calculate the efficiency or the current/voltage characteristic.
- Default
The partial load values are calculated automatically. Either the PV*SOL® model or the two-diode model is used to calculate the efficiency or the current/voltage characteristic.
PV*SOL® model
Normally the PV*SOL®-own partial load model is used, which achieves very good accuracy for most module technologies.
The model is used as standard for all technologies except those based on mono- and polycrystalline silicon.
The PV*SOL® model calculates rather too low tensions at low irradiations and estimates the energy yield very conservatively.
Two-diode model
For mono- and polycrystalline silicon-based modules, the two-diode model is used if all the necessary conditions are met.
For these module types, the two-diode model provides the most accurate results for the electrical quantities.
The deviations between the two-diode model and the measurement are in the range of measurement uncertainty.
The conditions for using the two diode model are as follows:
- The module uses crystalline silicon cells (mono or poly)
- The number of cells is given and greater than 10
For further information on the characteristic models used, see Calculation > PV modules > Characteristic curve models.
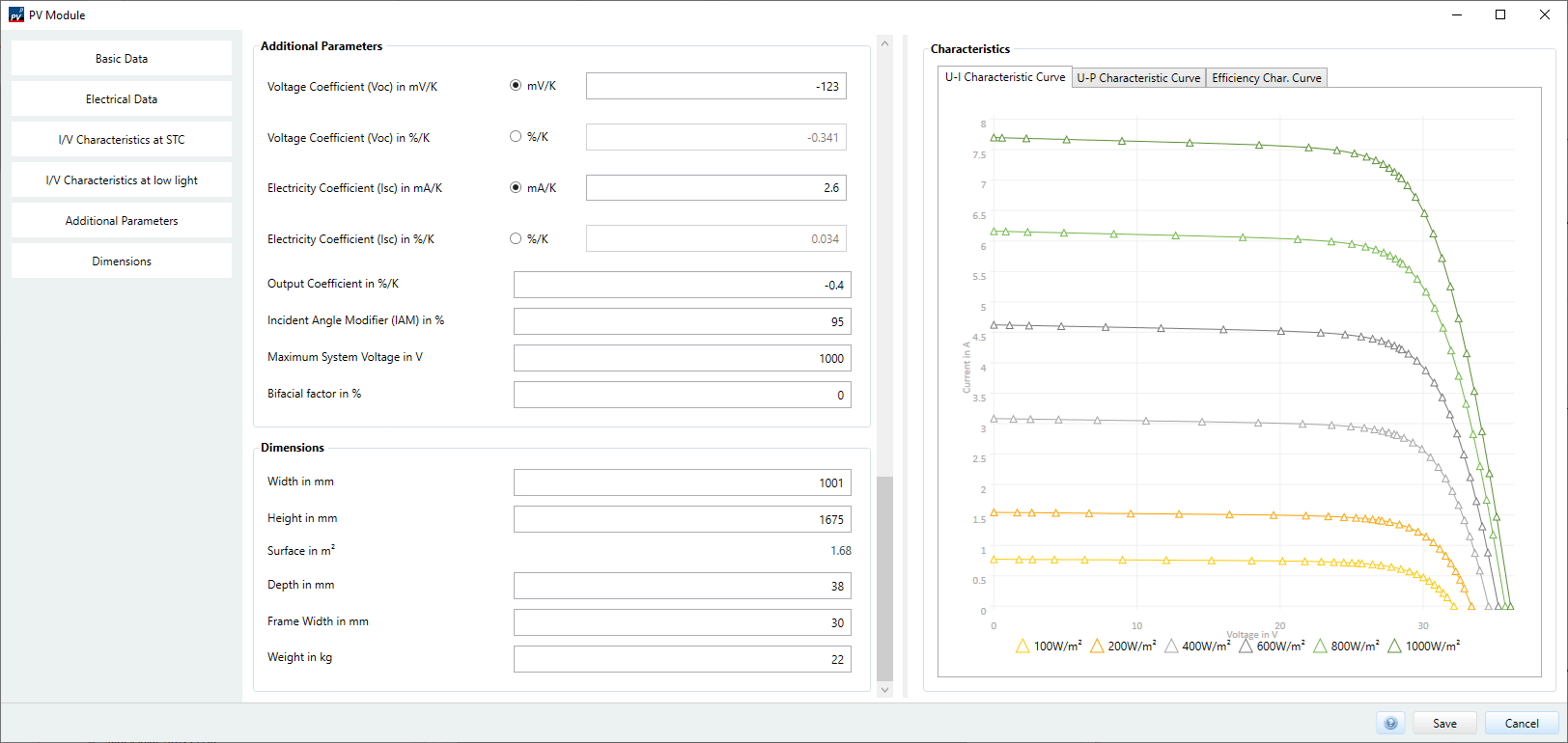
Further parameters
Here you define further important characteristics of the PV module.
- Voltage coefficient (Uoc)
This value indicates how the module voltage changes when the module temperature increases by one degree Celsius or Kelvin respectively. As the module temperature rises, the voltage decreases, the coefficient is negative. - Current coefficient (Isc)
This value indicates how the module current changes when the module temperature increases by one degree Celsius or Kelvin respectively. With increasing module temperature the current increases, the coefficient is positive. - Power coefficient
This value indicates how the module output changes when the module temperature increases by one degree Celsius or Kelvin respectively. Since the module voltage decreases more strongly than the module current when the temperature increases, the power decreases with increasing temperature. The coefficient is negative. - Angle correction factor
Part of the sunlight is reflected when it hits the glass of the PV module. The reflection depends on the angle at which the light strikes the module. The angle correction factor is used to calculate the reflection for each angle. - Maximum system voltage
This value specifies the maximum system voltage and must not be exceeded for safety reasons. This mainly affects the series connection of PV modules. - Bifacial factor
The bifacial factor indicates the proportion of backside irradiation that a module can process to generate electricity. For conventional monofacial modules, this value is 0 because the back side is inactive. With bifacial modules, the value is usually between 70 and 80%.
Mechanical variables
Here you define the dimensions and weight of the PV module. This information is required for the module allocation in the 3D design (see Pages > 3D Design).
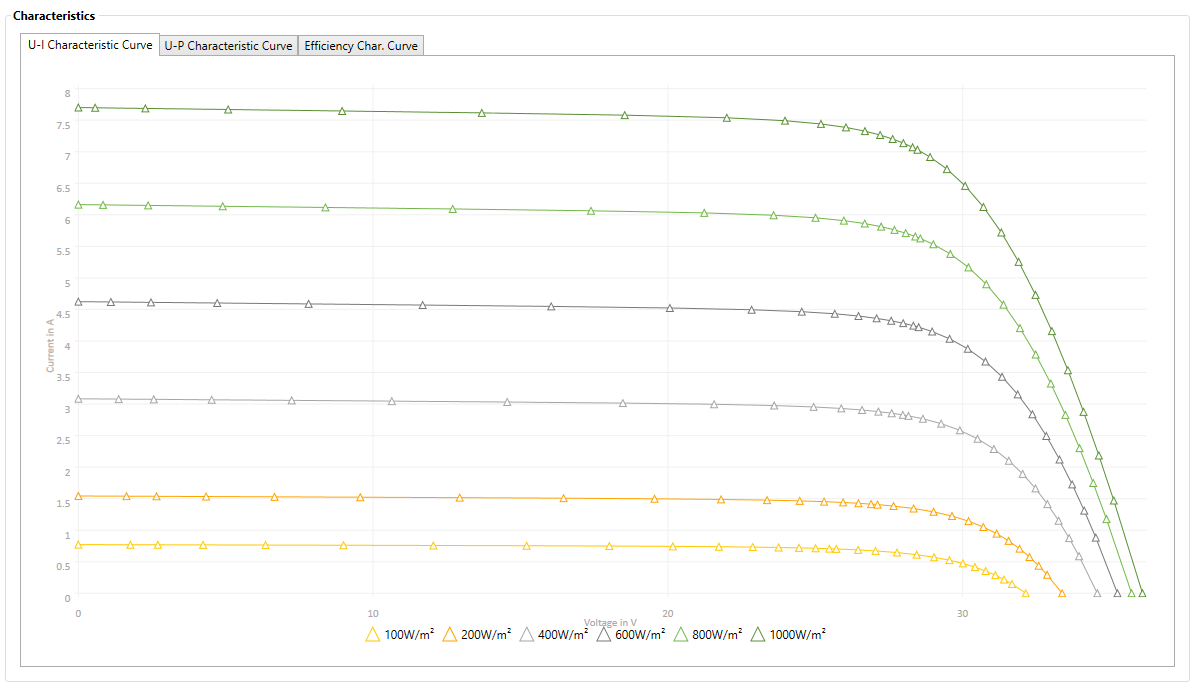
Characteristics
The resulting PV module characteristics are displayed here. You can choose from:
- UI characteristics
Module current as a function of module voltage, with variable module temperature and irradiation. - UP-characteristic curves
Module output as a function of module voltage, with variable module temperature and irradiation. - eta characteristics
relative efficiency as a function of irradiation
See also