Electric vehicles
Electric vehicles can be defined on the Electric Vehicles page
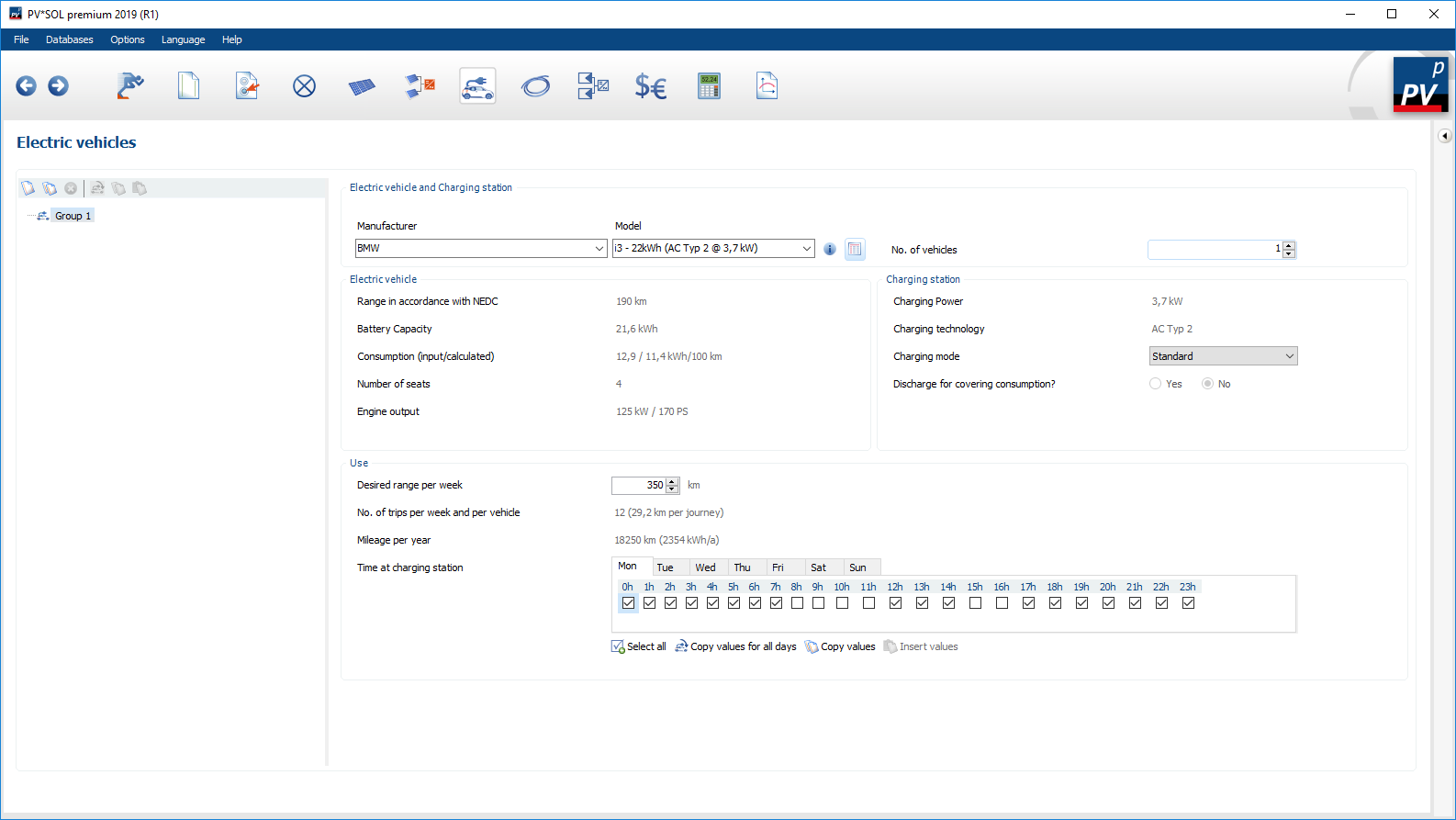
![]() . Different electric vehicles or vehicles with different user behaviour can be created in groups. In each group the number of vehicles can be defined in addition to the selection of the manufacturer and the vehicle model. The parameters of the vehicles and the charging station are specified by the manufacturers.
. Different electric vehicles or vehicles with different user behaviour can be created in groups. In each group the number of vehicles can be defined in addition to the selection of the manufacturer and the vehicle model. The parameters of the vehicles and the charging station are specified by the manufacturers.
You can edit the group list on the right side with the buttons in the selection bar
 . You can create new groups, duplicate or delete existing ones, transfer values from one group to all others or copy values from one group to paste them into another group.
. You can create new groups, duplicate or delete existing ones, transfer values from one group to all others or copy values from one group to paste them into another group.
To select an electric vehicle, use the dropdown menus Manufacturer and Model. Via the button
 you will receive detailed information about the selected electric vehicle. Alternatively, click the
you will receive detailed information about the selected electric vehicle. Alternatively, click the
 button to access the database. There you can select the desired electric vehicle.
button to access the database. There you can select the desired electric vehicle.
If the desired electric vehicle is not available in the database, you can create your own data records and use them.
Usage
Important input parameters are the usage times of the vehicle. For example, how much mileage you would like to cover with the vehicle per day and at what times the vehicle is at the charging station of the system.
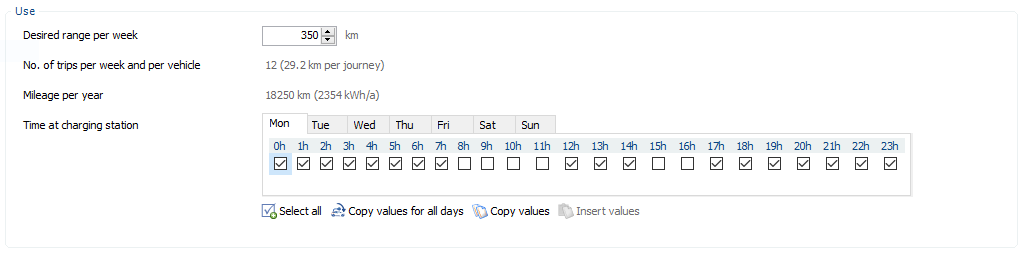
- Desired range per week
Enter here how many miles per week should be driven by car.- This results in the number of trips per week and the average of driven kilometres per journey.
- For information, the mileage per year is shown below.
- Charging station time
Here you can determine for each hour for each day of a week whether the car is at the charging station or not. A check mark means that the car is available and can be loaded if required.
Charging mode
In the charging mode you have the choice between two different types of charging:
- Default
The car is charged immediately when it is at the charging station. If there is not enough PV energy available at this time, it is charged from the grid. - PV optimized
In this mode, the car is only charged when PV energy is available. Only when charging from the mains is unavoidable in order to ensure that the battery is sufficiently charged for the next journey, is charging from the mains. This mode can significantly increase the solar share of the car battery charge.
Automatic phase switching
Charging stations for electric vehicles, such as wallboxes, usually have a minimum charging power that depends on the number of phases and the mains voltage. If a wallbox is connected to one phase at 230 V mains voltage, the minimum charging power is approx. 1.38 kW (230 V * 6 A). If it is connected to three phases, the minimum charging power is 4.14 kW (230 V * 6A * 3).
This means that the electric vehicle cannot be charged with PV energy as long as it is below the minimum charging power. With a 3-phase connection, this threshold is very high at over 4 kW, which is why many wallbox manufacturers offer automatic phase switching.
Automatic phase switching means that the charging station automatically switches between single-phase and three-phase charging as soon as a predefined threshold value is reached. This makes it possible, for example, to prevent unwanted charging interruptions if the PV system temporarily generates less power than is required for fast 3-phase charging.
See also